Sedative Interactions: What You Need to Know About Mixing Medications
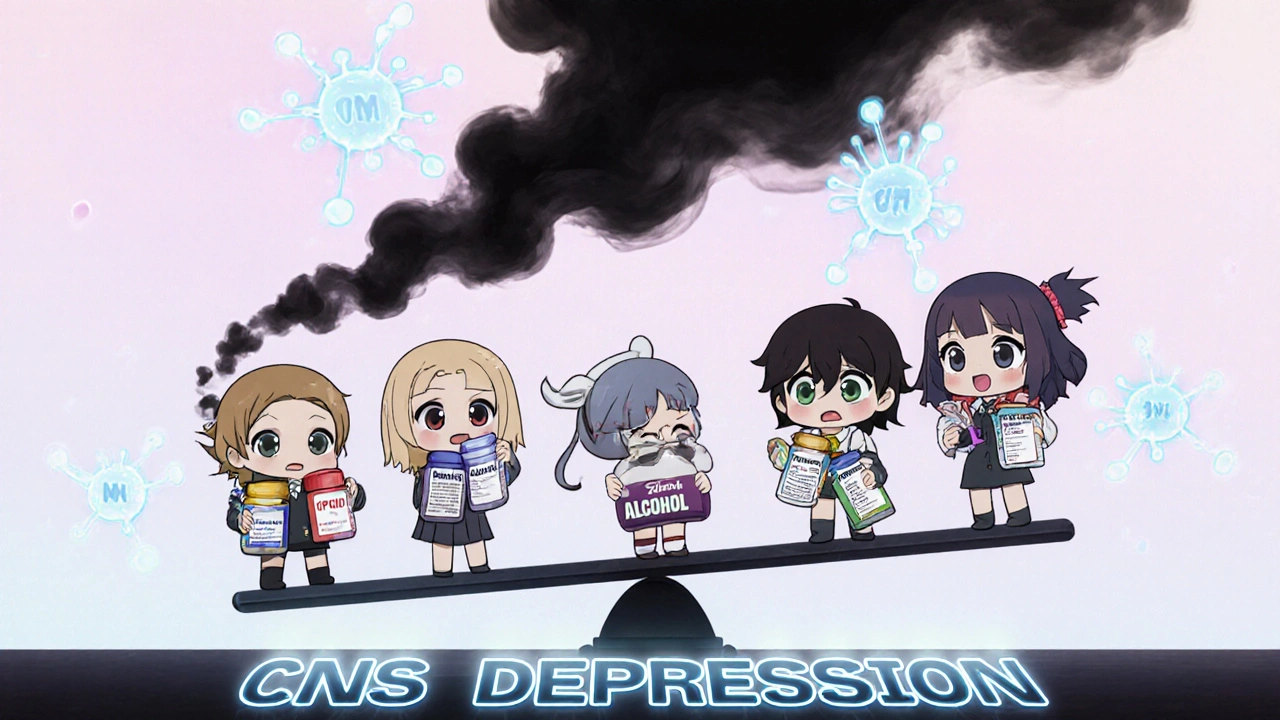
When you take a sedative, a drug that slows down brain activity to reduce anxiety, induce sleep, or relax muscles. Also known as central nervous system depressants, they include common prescriptions like diazepam, lorazepam, and zolpidem, as well as over-the-counter sleep aids and even alcohol. These drugs work by boosting GABA, a calming chemical in your brain—but when combined with other sedatives, that calming effect can turn deadly. The real danger isn’t taking one sedative alone—it’s mixing them. People don’t always realize that a nighttime painkiller with diphenhydramine, a glass of wine, or even an antihistamine for allergies can stack up with their prescribed sleep medicine. That’s not just a bad idea—it’s a risk for respiratory failure, coma, or death.
Sedative interactions don’t just happen with other sedatives. They also clash with benzodiazepines, a class of drugs used for anxiety, seizures, and muscle spasms, especially when paired with opioids like oxycodone or hydrocodone. The FDA has warned that this combo is one of the leading causes of accidental overdose deaths. Even sleep aids, including melatonin supplements and herbal remedies like valerian root, can add up if you’re already on a prescription sedative. And don’t forget alcohol—it’s the most common and underestimated partner in dangerous sedative interactions. One drink might seem harmless, but with a sedative, it can cut your breathing rate in half.
Some people think they’re being smart by taking a little extra to fall asleep faster, or doubling up because their medicine "doesn’t work anymore." But tolerance doesn’t make you safer—it makes you more vulnerable. Your body doesn’t adjust in a way that prevents overdose; it just means you need more to feel the same effect, pushing you closer to the edge. And if you’re older, or have liver or lung problems, your body clears these drugs slower, making interactions even riskier. The same goes for people taking multiple meds for chronic conditions—like epilepsy, depression, or heart disease—where sedatives are often part of the mix.
What you’ll find below are real, practical guides from people who’ve been there. Articles break down how common drugs like diazepam, zolpidem, and even OTC cold medicines can interact with each other—and with things you might not think of as dangerous, like grapefruit juice or herbal teas. You’ll see comparisons between sleep aids, warnings about mixing with alcohol, and what to do if you’ve already combined something risky. No fluff. No marketing. Just clear, direct info from trusted sources that help you avoid mistakes before they happen. These aren’t theoretical warnings—they’re based on real cases, FDA alerts, and clinical guidelines. If you’re taking any kind of sedative, this collection could literally save your life.